Exploring The Wonders Of Slope 2: A Comprehensive Guide
This article delves into the intricacies of slope 2, exploring its origins, applications, and significance in today's world. By the end, you'll have a clear grasp of why this concept matters and how it shapes the world around us. The journey of understanding slope 2 begins with its definition. In simple terms, slope 2 refers to the steepness or incline of a line in a two-dimensional space. It is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus, where it helps determine the rate of change between two variables.
Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, influencing everything from construction projects to technological advancements. By examining slope 2 in detail, we can uncover its hidden potential and appreciate its versatility.
To fully appreciate slope 2, it’s essential to explore its multifaceted nature. From its role in shaping linear equations to its influence on real-world scenarios, slope 2 offers a wealth of knowledge waiting to be unlocked.
Read also:Discovering The Glamorous World Of Saleh Dubai Bling A Complete Guide
In the sections ahead, we will break down this concept into digestible parts, answering common questions and providing practical insights. By the end of this guide, you'll not only understand slope 2 but also see how it connects to broader ideas and industries.
Table of Contents
- What Is Slope 2 and Why Does It Matter?
- The Mathematics Behind Slope 2
- How Is Slope 2 Used in Real Life?
- What Are the Common Misconceptions About Slope 2?
- Slope 2 in Technology and Engineering
- Can Slope 2 Help in Solving Complex Problems?
- Slope 2 and Its Impact on Modern Science
- Frequently Asked Questions About Slope 2
What Is Slope 2 and Why Does It Matter?
Slope 2 is more than just a mathematical term; it is a gateway to understanding relationships between variables. In essence, slope 2 measures the rate at which one quantity changes concerning another. For instance, if you're analyzing the speed of a moving object over time, slope 2 helps quantify how quickly the object is accelerating or decelerating.
Why does slope 2 matter? The answer lies in its versatility. It is used in countless industries, from architecture to economics. Architects rely on slope 2 to design safe and functional structures, while economists use it to predict market trends. Without slope 2, many of the technological advancements we take for granted today would not exist.
Consider this: slope 2 is the foundation of calculus, a branch of mathematics that deals with change and motion. By mastering slope 2, you gain the tools to tackle complex problems in physics, engineering, and beyond. Its importance cannot be overstated, making it a must-know concept for anyone interested in problem-solving.
Key Applications of Slope 2
- Construction: Calculating inclines for roads and ramps.
- Technology: Designing algorithms for machine learning.
- Physics: Understanding velocity and acceleration.
- Business: Forecasting sales and market trends.
The Mathematics Behind Slope 2
To truly grasp slope 2, it’s essential to explore its mathematical foundations. At its core, slope 2 is calculated using the formula: (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁). This formula determines the rise (vertical change) over the run (horizontal change) between two points on a graph. The result is a numerical value that indicates the steepness of the line.
For example, a slope 2 value of 2 means that for every unit increase in the x-axis, the y-axis increases by 2 units. Conversely, a negative slope 2 value indicates a downward trend. Understanding these principles is crucial for solving equations and interpreting graphs.
Read also:Elizabeth Keadle A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life Achievements And Legacy
Let’s break it down further. Slope 2 is not just about numbers; it’s about relationships. When applied to linear equations, slope 2 helps identify patterns and trends. This is particularly useful in fields like statistics, where identifying correlations between variables is key to making informed decisions.
How to Calculate Slope 2
- Identify two points on the line: (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂).
- Subtract the y-coordinates: y₂ - y₁.
- Subtract the x-coordinates: x₂ - x₁.
- Divide the difference in y-coordinates by the difference in x-coordinates.
Why Is Slope 2 So Important in Algebra?
In algebra, slope 2 is the backbone of linear equations. It helps define the relationship between variables, making it easier to predict outcomes and solve problems. Without slope 2, equations like y = mx + b would lose their meaning, leaving us without a clear way to model real-world scenarios.
How Is Slope 2 Used in Real Life?
Slope 2 isn’t confined to textbooks; it plays a vital role in everyday life. From designing roads to optimizing supply chains, its applications are vast and varied. For instance, civil engineers use slope 2 to ensure that roads have the correct incline for safety and efficiency. A steep slope 2 could lead to accidents, while a shallow one might cause waterlogging.
In the world of technology, slope 2 is equally indispensable. Machine learning algorithms rely on slope 2 to identify patterns in data. By analyzing the rate of change between variables, these algorithms can make predictions and recommendations. This is how platforms like Netflix and Amazon tailor suggestions to individual users.
Even in sports, slope 2 has its place. Coaches use it to analyze player performance, tracking improvements or declines over time. By plotting data points and calculating slope 2, they can identify areas for improvement and develop targeted training programs.
Examples of Slope 2 in Action
- Construction: Designing wheelchair-accessible ramps.
- Healthcare: Monitoring patient recovery rates.
- Finance: Predicting stock market trends.
What Are the Common Misconceptions About Slope 2?
Despite its widespread use, slope 2 is often misunderstood. One common misconception is that slope 2 only applies to straight lines. While it’s true that slope 2 is most commonly associated with linear equations, it can also be used to approximate non-linear relationships. This is achieved by breaking down curves into smaller segments and calculating the slope 2 for each.
Another misconception is that slope 2 is always positive. In reality, slope 2 can be positive, negative, zero, or undefined. A positive slope 2 indicates an upward trend, while a negative slope 2 signifies a downward trend. A slope 2 of zero means the line is horizontal, and an undefined slope 2 occurs when the line is vertical.
Finally, many people believe that slope 2 is only relevant in mathematics. However, as we’ve seen, its applications extend far beyond the classroom. From technology to healthcare, slope 2 is a powerful tool that shapes the world we live in.
Debunking Myths About Slope 2
- Myth: Slope 2 is only for straight lines.
Reality: It can approximate curves too. - Myth: Slope 2 is always positive.
Reality: It can be negative, zero, or undefined.
Slope 2 in Technology and Engineering
In the realm of technology and engineering, slope 2 is a game-changer. Engineers use it to design everything from bridges to roller coasters. By calculating slope 2, they can ensure that structures are safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing. For example, a roller coaster’s slope 2 determines the thrill factor, balancing excitement with safety.
Technology also benefits greatly from slope 2. In the field of robotics, slope 2 is used to program movements and predict outcomes. Autonomous vehicles rely on slope 2 to navigate roads and avoid obstacles. By analyzing the slope 2 of the terrain, these vehicles can adjust their speed and trajectory accordingly.
Even in software development, slope 2 plays a role. Algorithms that rely on slope 2 can optimize processes, making them faster and more efficient. This is particularly important in industries like logistics, where time is of the essence.
How Engineers Use Slope 2
- Designing safe and functional structures.
- Programming autonomous vehicles.
- Optimizing supply chain logistics.
Can Slope 2 Help in Solving Complex Problems?
Absolutely. Slope 2 is a powerful tool for tackling complex problems, especially in fields like physics and economics. By analyzing the rate of change between variables, slope 2 provides insights that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, physicists use slope 2 to study motion, calculating velocity and acceleration to understand how objects move through space.
In economics, slope 2 helps predict market trends. By plotting data points and calculating slope 2, analysts can identify patterns and make informed decisions. This is particularly useful in volatile markets, where understanding the rate of change can mean the difference between profit and loss.
Even in everyday life, slope 2 can simplify decision-making. For example, if you’re trying to decide between two investment options, calculating the slope 2 of their returns can help you choose the better option. This practical application makes slope 2 an invaluable tool for problem-solving.
Real-World Problem Solving with Slope 2
- Predicting market trends in economics.
- Studying motion in physics.
- Making informed investment decisions.
Slope 2 and Its Impact on Modern Science
Modern science owes much to slope 2. From biology to astronomy, slope 2 helps researchers analyze data and draw conclusions. In biology, for instance, slope 2 is used to study population growth. By plotting data points and calculating slope 2, scientists can predict how populations will change over time.
In astronomy, slope 2 plays a role in understanding celestial motion. By analyzing the slope 2 of a planet’s orbit, astronomers can determine its speed and trajectory. This information is crucial for planning space missions and studying the universe.
Even in environmental science, slope 2 is indispensable. Researchers use it to study climate change, tracking the rate of temperature increase over time. This data helps policymakers make informed decisions about environmental policies.
Scientific Applications of Slope 2
- Studying population growth in biology.
- Analyzing celestial motion in astronomy.
- Tracking climate change in environmental science.
Frequently Asked Questions About Slope 2
What is the difference between slope 1 and slope 2?
Slope 1 typically refers to a basic understanding of slope, focusing on simple linear equations. Slope 2, on the other hand, delves deeper, exploring more complex applications and relationships. While slope 1 is foundational, slope 2 is about mastering the concept and applying it to real-world scenarios.
Can slope 2 be negative?
Yes, slope 2 can be negative. A negative slope 2 indicates a downward trend, where the y-values decrease as the x-values increase. This is common in scenarios like declining stock prices or decreasing temperatures.
How is slope 2 used in machine learning?
Who Is Atticus Shaffer's Partner? A Comprehensive Guide To His Life And Career
Exploring The Eepy Meaning: What Does It Truly Signify?
Understanding Dua Lipa Deepfakes: Risks, Realities, And Solutions
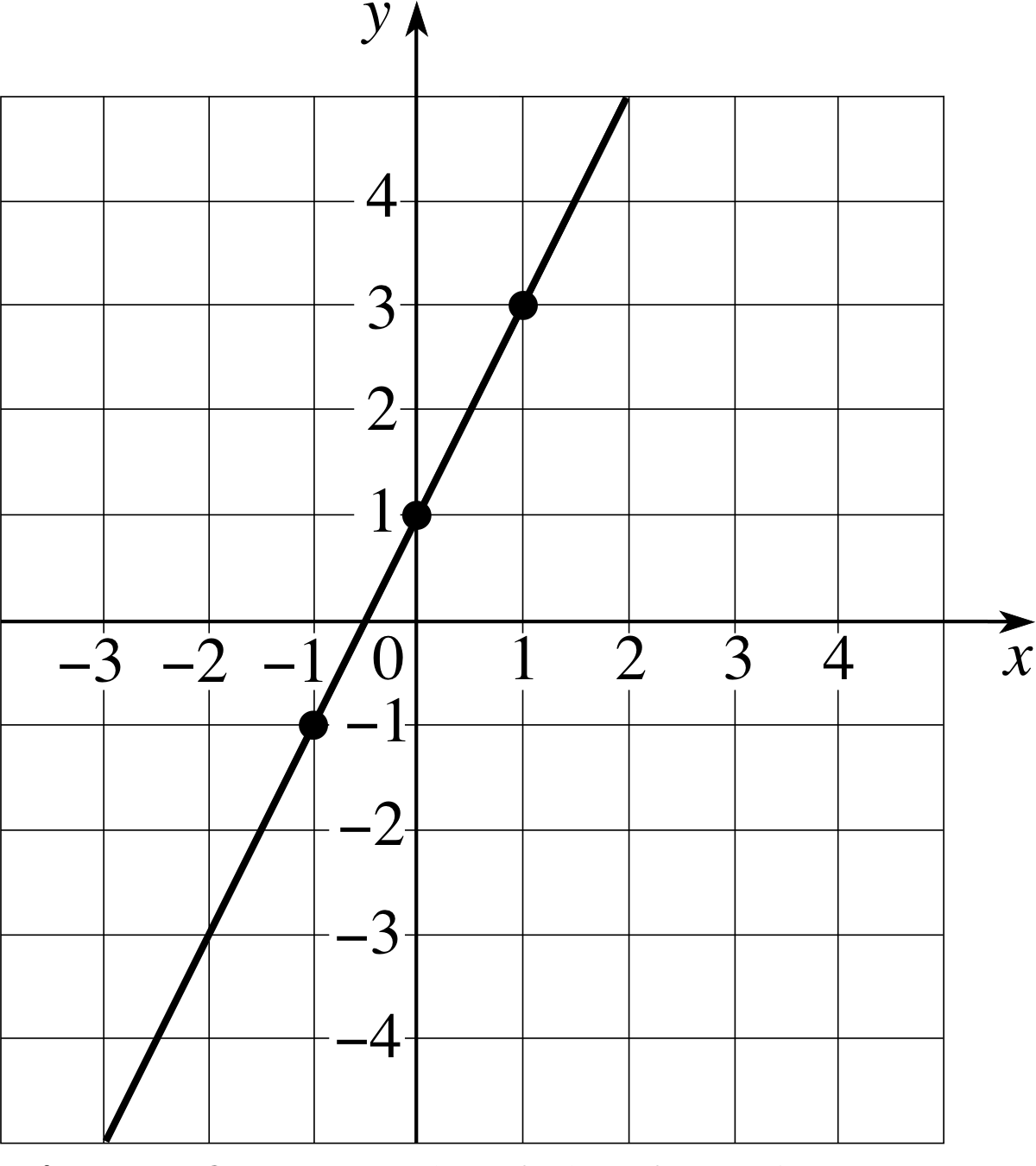
Slope Jeopardy Template
File2.1 Slope illustration.jpg RCABC Roofing Practices Manual