Understanding The Earth's Radius: A Comprehensive Guide
The Earth's radius is a fundamental measurement in understanding our planet's size and shape. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the world we live in, knowing the Earth's radius provides valuable insights into geography, geology, and even space exploration. This article will delve into the intricacies of the Earth's radius, offering a detailed exploration of its significance, variations, and applications.
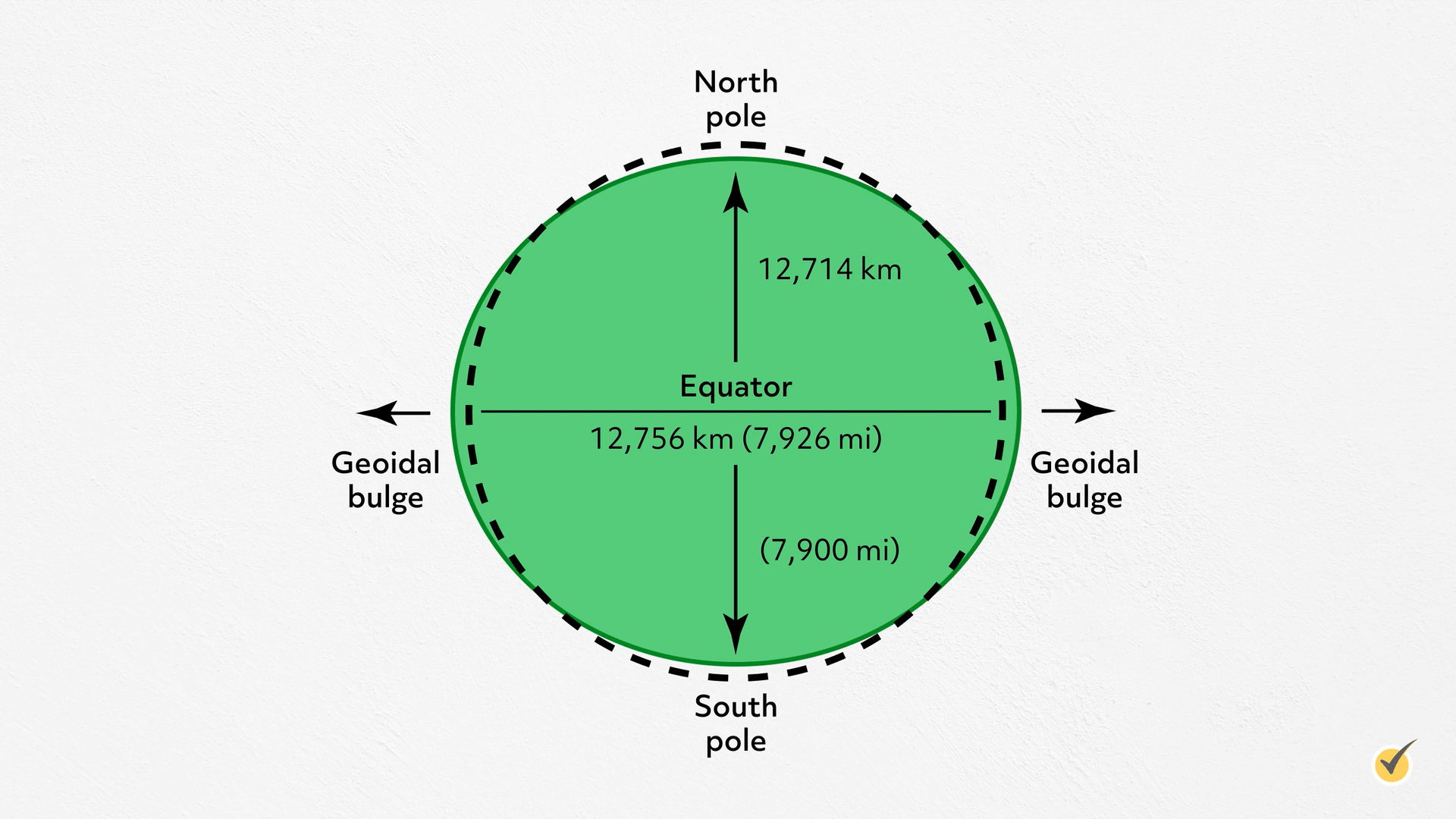
The concept of the Earth's radius might seem straightforward, but it is more complex than it appears. The Earth is not a perfect sphere; it is an oblate spheroid, meaning it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. This unique shape has significant implications for how we measure and understand the Earth's dimensions. By examining various aspects of the Earth's radius, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the planet's physical characteristics and the science behind them.
In this article, we will explore the Earth's radius in detail, breaking down its different types, how they are measured, and why they matter. From historical methods of measurement to modern techniques involving satellites, we will cover the evolution of our understanding of the Earth's size. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the Earth's radius and its importance in various scientific fields.
Read also:Austin North Unveiling The Rising Stars Journey And Achievements
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Earth's Radius
- Types of Earth's Radius
- Historical Measurements of Earth's Radius
- Modern Measurement Techniques
- Applications in Geography
- Earth's Radius in Space Exploration
- Significance in Climate Studies
- Earth's Radius and Navigation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction to Earth's Radius
The Earth's radius is the distance from the planet's center to its surface. However, due to the Earth's oblate spheroid shape, this measurement varies depending on the location. The Earth's radius is crucial for understanding its geometry, as it influences calculations in geography, astronomy, and physics.
There are several ways to define the Earth's radius, including the equatorial radius, polar radius, and mean radius. Each of these measurements provides a different perspective on the Earth's size and shape. Understanding these variations is essential for accurate scientific and practical applications.
Why the Earth's Radius Matters
The Earth's radius is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical implications in many fields. For example, in geography, the radius is used to calculate distances and areas. In space exploration, it helps determine the trajectories of satellites and spacecraft. Additionally, the Earth's radius plays a role in climate studies, as it affects the distribution of sunlight and heat across the planet.
Types of Earth's Radius
The Earth's radius can be categorized into three main types: equatorial radius, polar radius, and mean radius. Each type serves a specific purpose and provides unique insights into the planet's dimensions.
Equatorial Radius
The equatorial radius is the distance from the Earth's center to the equator. It is the longest radius due to the planet's bulging at the equator. The equatorial radius is approximately 6,378.1 kilometers (3,963.2 miles).
Polar Radius
The polar radius is the distance from the Earth's center to the poles. It is shorter than the equatorial radius because the Earth is flattened at the poles. The polar radius measures about 6,356.8 kilometers (3,949.9 miles).
Read also:Ringo Starrs Date Of Birth A Comprehensive Guide To The Legendary Drummers Life And Career
Mean Radius
The mean radius is the average of all radii measured from the Earth's center to its surface. It is often used in calculations where a single value is needed to represent the Earth's size. The mean radius is approximately 6,371 kilometers (3,959 miles).
Historical Measurements of Earth's Radius
Throughout history, humans have sought to measure the Earth's radius using various methods. Early attempts date back to ancient civilizations, with notable contributions from Greek scholars like Eratosthenes.
Eratosthenes' Experiment
Eratosthenes, a Greek mathematician and geographer, conducted one of the earliest known measurements of the Earth's radius around 240 BCE. He used the angle of the sun's rays at two different locations to calculate the Earth's circumference, from which the radius could be derived.
Modern Historical Advances
Over the centuries, advancements in technology and mathematics have refined our understanding of the Earth's radius. The invention of the telescope and the development of trigonometry allowed for more accurate measurements. By the 19th century, geodetic surveys and triangulation methods provided precise data on the Earth's dimensions.
Modern Measurement Techniques
Today, scientists use advanced technologies to measure the Earth's radius with unprecedented accuracy. These techniques include satellite-based systems, GPS, and radar altimetry.
Satellite Measurements
Satellites equipped with radar and laser altimeters can measure the Earth's surface with incredible precision. These instruments provide data on the planet's topography, allowing scientists to calculate the radius at various locations.
GPS Technology
The Global Positioning System (GPS) has revolutionized our ability to measure distances and locations on Earth. By triangulating signals from multiple satellites, GPS devices can determine positions with high accuracy, contributing to our understanding of the Earth's radius.
Applications in Geography
The Earth's radius is a critical parameter in geography, influencing calculations of distances, areas, and volumes. It is used in mapping, cartography, and geographic information systems (GIS).
Mapping and Cartography
Accurate knowledge of the Earth's radius is essential for creating maps and charts. Cartographers use this information to project the Earth's surface onto flat maps, ensuring that distances and scales are correct.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS relies on precise measurements of the Earth's dimensions to analyze spatial data. The Earth's radius is used in calculations for terrain modeling, urban planning, and environmental studies.
Earth's Radius in Space Exploration
The Earth's radius plays a vital role in space exploration, particularly in determining the trajectories of satellites and spacecraft. Understanding the planet's dimensions helps scientists plan missions and ensure safe re-entry into the atmosphere.
Satellite Orbits
Satellites orbit the Earth at various altitudes, depending on their purpose. The Earth's radius is used to calculate the orbital parameters, ensuring that satellites remain in stable orbits.
Spacecraft Trajectories
When planning missions to other planets or celestial bodies, scientists must account for the Earth's radius. This information is used to calculate launch windows, trajectories, and fuel requirements.
Significance in Climate Studies
The Earth's radius is an important factor in climate studies, as it affects the distribution of sunlight and heat across the planet. Variations in the Earth's dimensions influence weather patterns and climate systems.
Seasonal Changes
The Earth's oblate spheroid shape contributes to seasonal changes, as the angle of sunlight varies throughout the year. The radius at different latitudes affects the intensity of solar radiation received.
Ocean Circulation
The Earth's radius influences ocean currents and circulation patterns. Variations in the planet's dimensions affect the gravitational forces that drive ocean movements, impacting global climate systems.
Earth's Radius and Navigation
Navigation relies heavily on accurate measurements of the Earth's radius. Whether traveling by land, sea, or air, understanding the planet's dimensions is essential for determining positions and distances.
Air and Sea Navigation
Pilots and sailors use the Earth's radius to calculate distances and plan routes. Nautical charts and aviation maps incorporate this information to ensure safe and efficient travel.
Global Positioning Systems (GPS)
As mentioned earlier, GPS technology depends on precise measurements of the Earth's radius. This system is used worldwide for navigation, tracking, and location-based services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about the Earth's radius:
What is the average radius of the Earth?
The average radius of the Earth is approximately 6,371 kilometers (3,959 miles).
Why is the Earth's radius not constant?
The Earth's radius varies because the planet is an oblate spheroid, meaning it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator.
How is the Earth's radius measured today?
Modern techniques for measuring the Earth's radius include satellite-based systems, GPS, and radar altimetry.
Conclusion
The Earth's radius is a fascinating and essential measurement that provides valuable insights into our planet's size and shape. From historical experiments to modern technologies, our understanding of the Earth's dimensions has evolved significantly over time. By exploring the different types of Earth's radius and their applications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the science behind our planet's geometry.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the Earth's radius. If you found this guide helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might be interested. Additionally, feel free to leave a comment or explore more articles on related topics to expand your knowledge further.
Fortnite Downed: Understanding The Causes, Impacts, And Solutions
Secret Party Luna: The Ultimate Guide To An Unforgettable Experience
Bridgit Mendler's Education: A Comprehensive Guide To Her Academic Journey
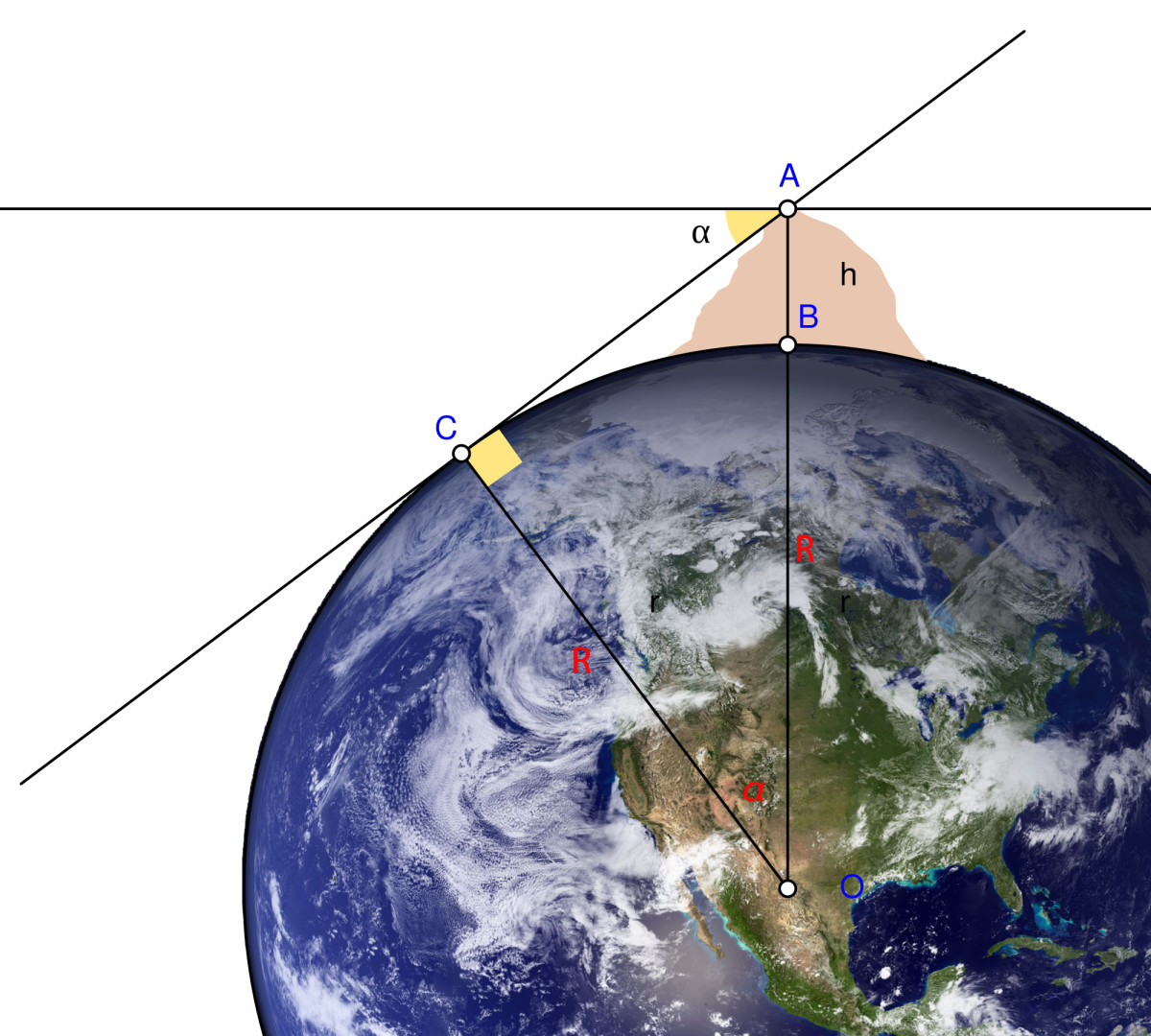
AlBiruni's Classic Experiment How to Calculate the Radius of the
Earth's Structure A Simple Exploration (Video)