Understanding Stop Limit Orders: A Comprehensive Guide For Traders
Stop limit orders are one of the most powerful tools in a trader's arsenal, offering a strategic way to manage risk and optimize trading outcomes. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting your journey in the stock market, understanding how to use stop limit orders effectively can make a significant difference in your trading performance. These orders combine the features of stop orders and limit orders, providing traders with greater control over their trades while mitigating potential losses. In today's volatile markets, mastering stop limit orders is essential for protecting your investments and maximizing profits.
For many traders, navigating the complexities of different order types can be overwhelming. However, stop limit orders offer a unique solution that bridges the gap between market orders and traditional limit orders. Unlike a standard market order that executes immediately at the current market price, or a basic limit order that may not execute if the market moves against you, stop limit orders provide a safety net. They ensure that your trade only executes within a specified price range, giving you peace of mind during unpredictable market conditions.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about stop limit orders, from their basic mechanics to advanced strategies. We'll explore how these orders work, their advantages and limitations, and provide practical examples to help you implement them effectively in your trading strategy. Whether you're looking to protect your portfolio from sudden market swings or seeking to capture profits at optimal price points, this article will equip you with the knowledge and tools to make informed trading decisions.
Read also:Brooke Bridges A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- What is a Stop Limit Order?
- How Stop Limit Orders Work
- Advantages of Using Stop Limit Orders
- Limitations and Risks of Stop Limit Orders
- Practical Examples of Stop Limit Orders
- Advanced Strategies for Stop Limit Orders
- Stop Limit vs. Other Order Types
- Best Practices for Using Stop Limit Orders
- Key Statistics and Market Insights
- Conclusion and Next Steps
What is a Stop Limit Order?
A stop limit order is a type of conditional trade that combines the features of a stop order and a limit order. It allows traders to specify both a stop price and a limit price for their trade. When the stop price is reached, the order becomes a limit order, which will only execute at the specified limit price or better. This dual mechanism provides traders with greater control over their trades while minimizing the risk of unfavorable price execution.
Stop limit orders are particularly useful in volatile markets where prices can fluctuate rapidly. By setting both a stop price and a limit price, traders can protect themselves from sudden price swings while ensuring that their trades are executed within a desired price range. For example, if a stock is trading at $50 and you set a stop price of $48 with a limit price of $47, the order will only execute if the stock price falls to $48 and then trades at $47 or higher.
Key Components of a Stop Limit Order
- Stop Price: The price at which the stop limit order is triggered.
- Limit Price: The maximum or minimum price at which the order will be executed.
- Order Duration: The time period during which the order remains active.
How Stop Limit Orders Work
Understanding the mechanics of stop limit orders is crucial for implementing them effectively in your trading strategy. The process begins when the market price of a security reaches the specified stop price. At this point, the stop limit order is triggered and becomes a limit order. The limit order will then attempt to execute at the specified limit price or better, depending on market conditions.
For example, let's say you own shares of a company trading at $100 per share. You want to protect your investment from significant losses, so you set a stop limit order with a stop price of $95 and a limit price of $94. If the stock price drops to $95, the stop limit order is triggered, and the system will attempt to sell your shares at $94 or higher. However, if the market is moving quickly, there's a possibility that your order may not be filled if the price drops below $94 before your trade executes.
Execution Process
- The market price reaches the stop price.
- The stop limit order is triggered and becomes a limit order.
- The limit order attempts to execute at the specified limit price or better.
- If the limit price cannot be met, the order remains unfilled.
Advantages of Using Stop Limit Orders
Stop limit orders offer several advantages that make them an attractive option for traders looking to manage risk and optimize their trading strategies. One of the primary benefits is the ability to set precise price parameters for trade execution. This feature allows traders to protect their investments from significant losses while ensuring that their trades are executed within a desired price range.
Another advantage of stop limit orders is their flexibility. Unlike market orders that execute immediately at the current market price, stop limit orders provide traders with greater control over when and at what price their trades are executed. This flexibility is particularly valuable in volatile markets where prices can fluctuate rapidly, making it challenging to execute trades at favorable prices.
Read also:What Country Is Faze Rug From Unveiling The Origins Of A Gaming Legend
Key Benefits
- Enhanced control over trade execution
- Protection against unfavorable price movements
- Flexibility to set specific price parameters
- Reduced risk of slippage compared to market orders
Limitations and Risks of Stop Limit Orders
While stop limit orders offer numerous advantages, they also come with certain limitations and risks that traders should be aware of. One of the primary limitations is the possibility of partial or no execution. If the market moves quickly past the specified limit price, the order may remain unfilled or only partially filled, leaving the trader exposed to potential losses.
Another risk associated with stop limit orders is the potential for missed opportunities. In fast-moving markets, the price may trigger the stop price but fail to reach the limit price, resulting in no execution. This scenario can be particularly frustrating for traders who are trying to protect their positions or capture profits at specific price points.
Common Risks
- Potential for partial or no execution
- Missed opportunities in fast-moving markets
- Complexity in setting appropriate price parameters
- Requires careful monitoring of market conditions
Practical Examples of Stop Limit Orders
To better understand how stop limit orders work in real-world scenarios, let's explore a few practical examples. These examples will illustrate how traders can use stop limit orders to protect their investments and optimize their trading strategies.
Example 1: Protecting Against Losses
Imagine you purchased shares of a tech company at $150 per share. To protect your investment from significant losses, you set a stop limit order with a stop price of $140 and a limit price of $138. If the stock price drops to $140, the stop limit order is triggered, and the system will attempt to sell your shares at $138 or higher. This setup ensures that you limit your potential losses while maintaining some flexibility in trade execution.
Example 2: Capturing Profits
Suppose you own shares of a pharmaceutical company trading at $200 per share. You want to lock in profits if the price rises but also protect against a sudden drop. You set a stop limit order with a stop price of $210 and a limit price of $208. If the stock price reaches $210, the order is triggered, and the system will attempt to sell your shares at $208 or higher. This strategy allows you to capture profits while minimizing the risk of missing out on favorable price movements.
Key Takeaways from Examples
- Use stop limit orders to protect against losses and capture profits.
- Set appropriate stop and limit prices based on market conditions.
- Monitor your orders regularly to ensure they are executed as intended.
Advanced Strategies for Stop Limit Orders
For experienced traders, stop limit orders can be used in more sophisticated ways to enhance trading performance. One advanced strategy involves using stop limit orders in combination with technical analysis to identify optimal entry and exit points. By analyzing price charts and technical indicators, traders can set stop limit orders at strategic levels to maximize their chances of successful trade execution.
Another advanced strategy is to use stop limit orders in pairs trading. This approach involves simultaneously buying one security and selling another that is correlated with it. By setting stop limit orders on both sides of the trade, traders can manage risk more effectively and capitalize on price discrepancies between the two securities.
Advanced Techniques
- Combine stop limit orders with technical analysis
- Use in pairs trading for enhanced risk management
- Implement trailing stop limits for dynamic price adjustments
- Utilize multiple stop limit orders for layered protection
Stop Limit vs. Other Order Types
Understanding the differences between stop limit orders and other order types is essential for making informed trading decisions. While stop limit orders offer unique advantages, they also have distinct characteristics that set them apart from market orders, limit orders, and stop orders.
Market Orders: Market orders execute immediately at the current market price, regardless of price fluctuations. While they provide speed and certainty of execution, they can result in unfavorable prices, especially in volatile markets. Stop limit orders, on the other hand, offer greater control over price execution but may not execute if the market moves quickly.
Limit Orders: Limit orders allow traders to specify the maximum price they are willing to pay or the minimum price they are willing to accept. However, they may not execute if the market price does not reach the specified limit price. Stop limit orders combine the features of limit orders with the triggering mechanism of stop orders, providing a balance between price control and execution certainty.
Comparison Table
| Order Type | Execution Speed | Price Control | Risk of Non-Execution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Order | Immediate | Low | None |
| Limit Order | Variable | High | High |
| Stop Order | Immediate after trigger | Low | None |
| Stop Limit Order | Variable after trigger | High | Moderate |
Best Practices for Using Stop Limit Orders
To maximize the effectiveness of stop limit orders, traders should follow several best practices. First, it's essential to set realistic stop and limit prices based on market conditions and your trading strategy. Avoid setting prices too close to the current market price, as this may result in premature triggering or missed opportunities.
Second, regularly monitor your stop limit orders to ensure they are still aligned with your trading goals. Market conditions can change rapidly, and adjustments may be necessary to maintain optimal risk management. Additionally, consider using trailing stop limits to dynamically adjust your stop price as the market moves in your favor, allowing you to capture more profits while protecting against losses.
Recommended Practices
- Set realistic stop and limit prices
- Monitor orders regularly for adjustments
- Use trailing stop limits for dynamic adjustments
- Combine with other risk management tools
Key Statistics and Market Insights
Understanding market trends and statistics can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of stop limit orders. According to a study by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), approximately 30% of retail traders use stop orders, including stop limit orders, to manage risk in their portfolios. This widespread adoption highlights the importance of these tools in modern trading strategies.
Additionally, research from the Securities and
Is Genovia Real? Unraveling The Mystery Behind The Fictional Kingdom
Appropriate Weight For 5'6 Male: A Comprehensive Guide To Achieving A Healthy Lifestyle
Cast Of True Beauty: Unveiling The Stars Behind The Hit K-Drama
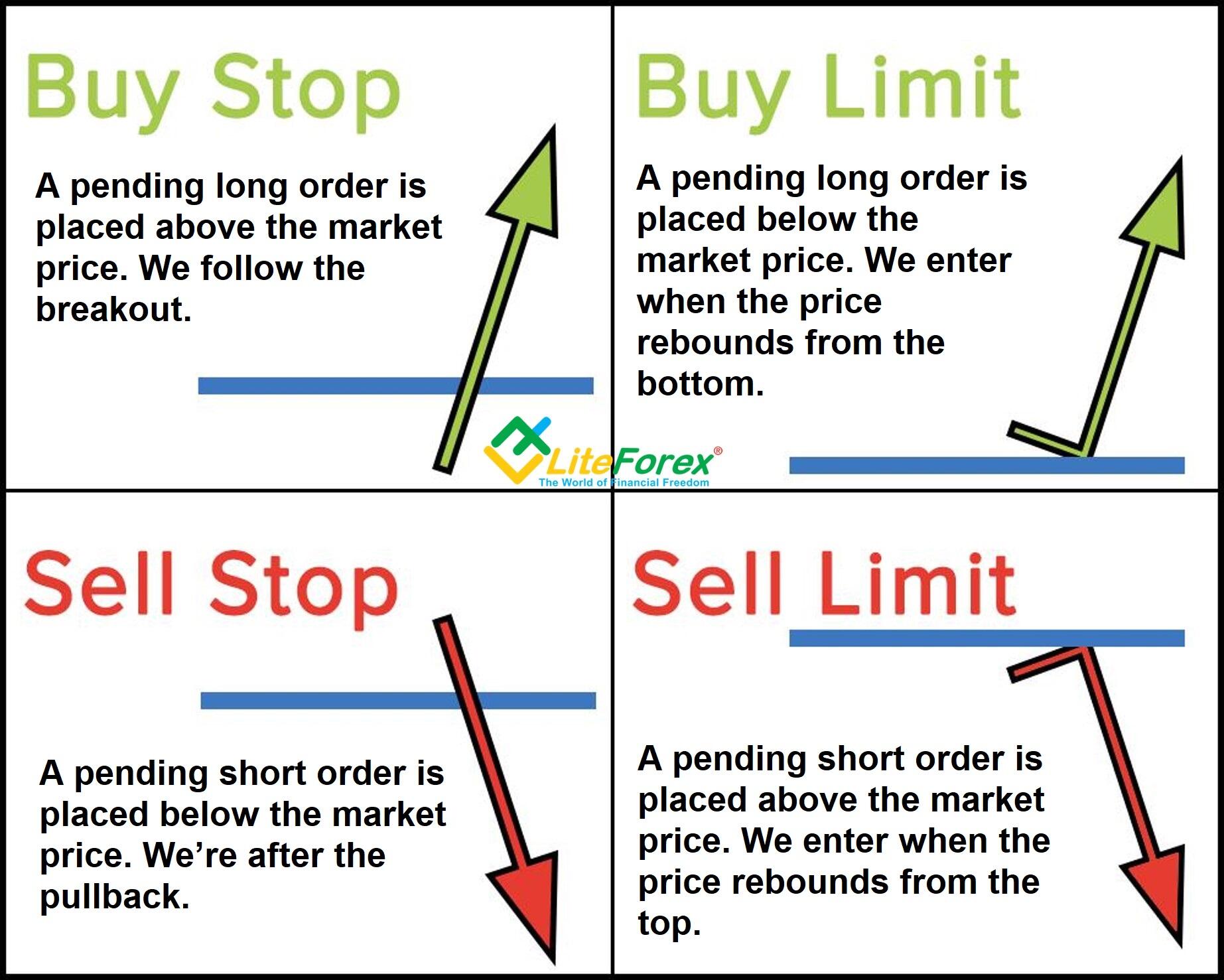
Types of Forex Orders Market, Limit, and Stop Buy and Sell Orders
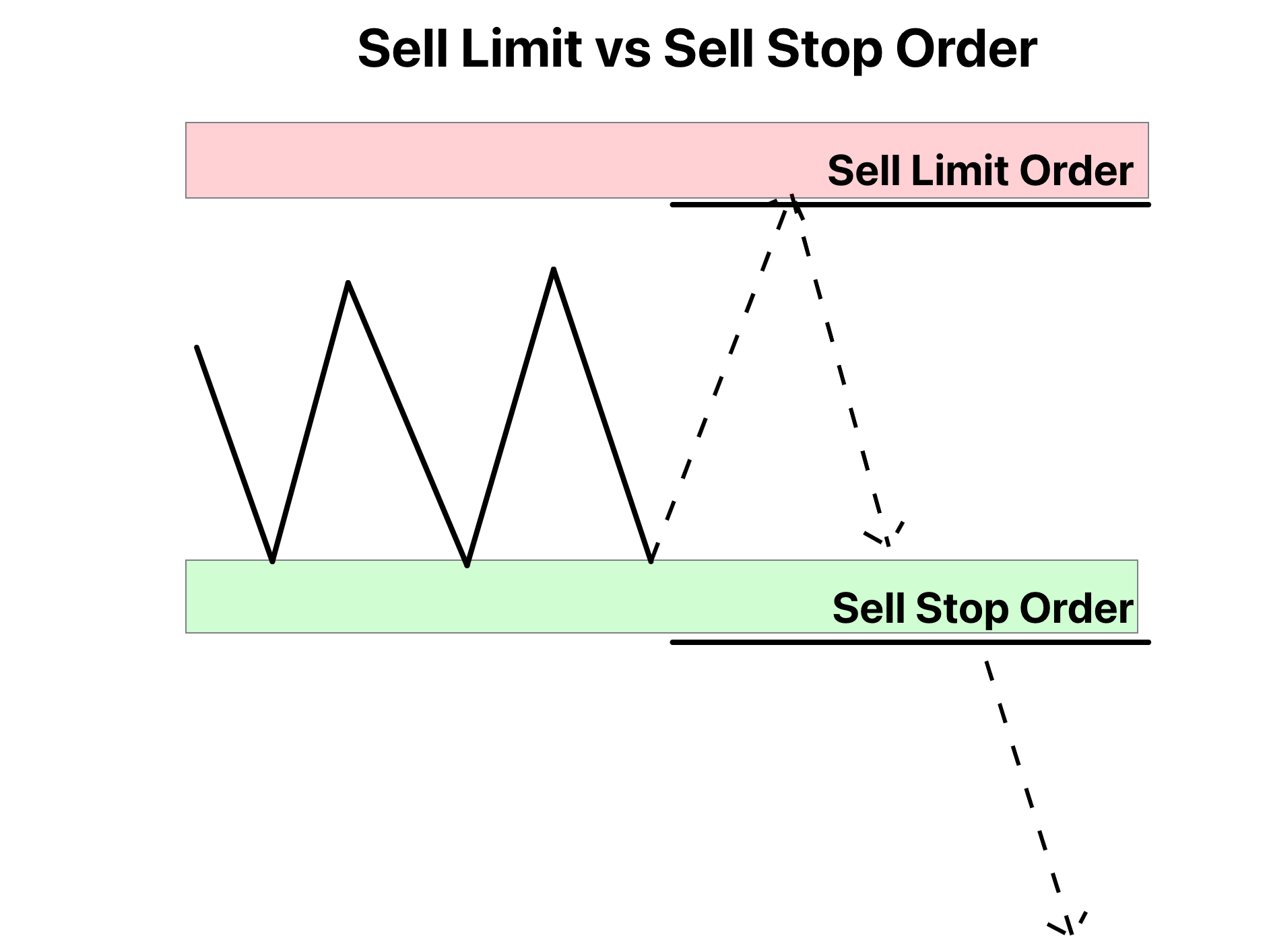
Sell limit order vs. sell stop order ForexBee