What Does BLM Land Mean? A Comprehensive Guide To Public Lands Managed By The Bureau Of Land Management
BLM land refers to public lands managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), a federal agency under the U.S. Department of the Interior. These lands are vast, diverse, and hold immense ecological, cultural, and economic significance. Understanding what BLM land means is crucial for anyone who enjoys outdoor recreation, cares about conservation, or is interested in natural resource management. BLM land spans over 245 million acres, primarily in the western United States, and plays a vital role in preserving America’s natural heritage.
Public lands managed by the BLM are often misunderstood or overlooked, despite their critical role in supporting ecosystems, wildlife, and local communities. These lands are open to a wide range of uses, including recreation, grazing, mining, and energy development, making them a cornerstone of sustainable land management. Whether you're planning a hiking trip, researching land use policies, or simply curious about the landscapes that define the American West, this guide will provide you with a thorough understanding of BLM land and its importance.
In this article, we’ll explore the history, purpose, and management practices of BLM land. We’ll also discuss its ecological significance, recreational opportunities, and the challenges it faces. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of what BLM land means and how it impacts both the environment and society. Let’s dive into the details and uncover the value of these remarkable public lands.
Read also:Xqc Investments A Comprehensive Guide To The Twitch Streamers Financial Ventures
Table of Contents
- What Is BLM Land?
- History of BLM Land
- Purpose and Management of BLM Land
- Ecological Significance of BLM Land
- Recreational Opportunities on BLM Land
- Challenges and Controversies Facing BLM Land
- Conservation Efforts and Initiatives
- How to Support and Protect BLM Land
- Frequently Asked Questions About BLM Land
- Conclusion
What Is BLM Land?
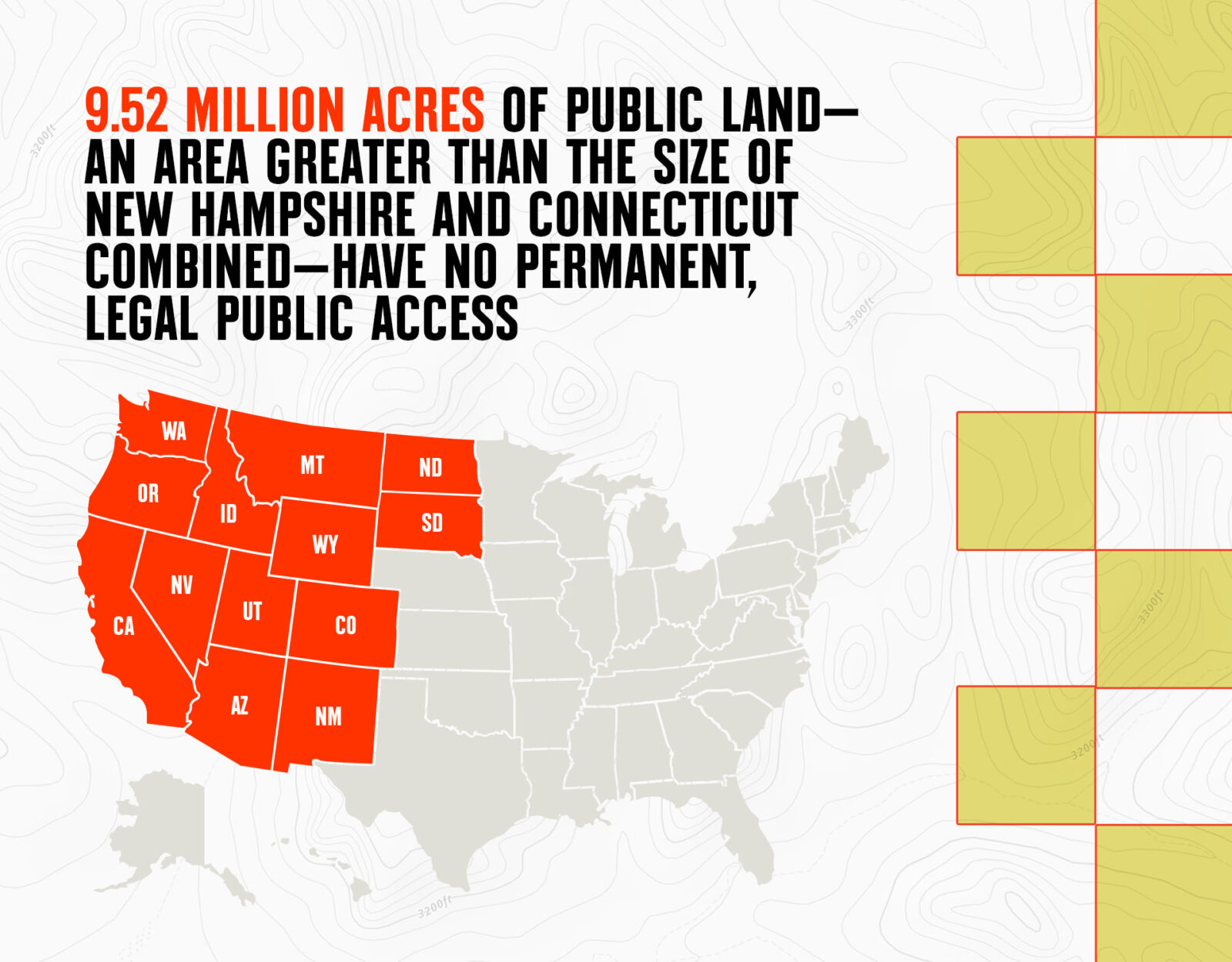
BLM land refers to the public lands managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), a federal agency responsible for overseeing approximately 245 million acres of land in the United States. These lands are primarily located in the western states, including Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming. BLM land makes up about 10% of the total land area in the U.S., making it one of the largest land management agencies in the country.
The primary mission of the BLM is to sustain the health, diversity, and productivity of public lands for the use and enjoyment of present and future generations. These lands are managed under a "multiple-use" mandate, which means they are open to a variety of activities, including recreation, grazing, mining, energy development, and conservation. This balanced approach ensures that BLM land serves both economic and environmental purposes.
One of the defining features of BLM land is its diversity. These lands encompass a wide range of ecosystems, from deserts and grasslands to forests and mountains. They are home to countless species of plants and animals, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. Additionally, BLM land contains significant cultural and historical resources, including ancient Native American sites, pioneer trails, and fossil-rich areas.
History of BLM Land
The history of BLM land dates back to the early days of the United States, when vast tracts of land were acquired through treaties, purchases, and wars. These lands were initially considered "public domain" and were available for settlement, agriculture, and resource extraction. Over time, the federal government began to recognize the need for organized management to prevent overuse and degradation of these valuable resources.
In 1946, the Bureau of Land Management was established through the merger of two agencies: the General Land Office and the Grazing Service. This new agency was tasked with managing public lands in a way that balanced competing interests, such as conservation, recreation, and economic development. Since then, the BLM has played a central role in shaping land use policies and practices in the United States.
Throughout its history, the BLM has faced numerous challenges, including conflicts over land use, environmental degradation, and funding limitations. Despite these challenges, the agency has made significant progress in improving land management practices and protecting natural and cultural resources. Today, BLM land continues to be a vital part of America’s public land system, providing opportunities for recreation, conservation, and sustainable resource use.
Read also:Result Bio Oil Stretch Marks The Ultimate Guide To Fading Stretch Marks Naturally
Purpose and Management of BLM Land
The purpose of BLM land is to serve the public interest by managing these lands in a way that balances multiple uses and values. This includes supporting economic activities, protecting natural resources, and providing recreational opportunities. To achieve this, the BLM follows a set of principles and practices designed to ensure sustainable land management.
The Multiple-Use Mandate
One of the core principles guiding the management of BLM land is the "multiple-use" mandate. This policy, established by the Federal Land Policy and Management Act (FLPMA) of 1976, requires the BLM to manage public lands for a variety of uses, including:
- Recreation: Activities such as hiking, camping, hunting, and fishing are popular on BLM land.
- Grazing: Livestock grazing is a traditional use of BLM land and is carefully regulated to prevent overgrazing.
- Energy Development: BLM land is a significant source of oil, gas, coal, and renewable energy resources.
- Conservation: Protecting wildlife habitats, watersheds, and cultural resources is a key priority.
By balancing these uses, the BLM aims to ensure that public lands remain productive and accessible for future generations.
Sustainable Management Practices
To achieve its goals, the BLM employs a range of sustainable management practices. These include:
- Land Use Planning: The BLM develops comprehensive land use plans that outline how specific areas will be managed.
- Environmental Monitoring: Regular assessments are conducted to track the health of ecosystems and identify potential issues.
- Public Involvement: The BLM actively engages with stakeholders, including local communities, tribes, and environmental groups, to ensure that management decisions reflect diverse perspectives.
These practices help the BLM fulfill its mission while addressing the complex challenges of managing public lands.
Ecological Significance of BLM Land
BLM land plays a critical role in maintaining the ecological balance of the United States. These lands are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are rare or endangered. They also provide essential ecosystem services, such as clean water, carbon storage, and habitat for pollinators.
One of the most significant ecological features of BLM land is its biodiversity. For example, the sagebrush ecosystems of the western United States, which are predominantly found on BLM land, support over 350 species of wildlife, including the iconic sage grouse. Similarly, the deserts of the Southwest are home to unique species like the desert tortoise and Joshua trees.
BLM land also plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change. These lands store vast amounts of carbon in their soils and vegetation, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, they provide opportunities for renewable energy development, such as solar and wind projects, which contribute to a cleaner energy future.
Recreational Opportunities on BLM Land
BLM land offers a wealth of recreational opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts. From hiking and camping to off-roading and wildlife watching, there’s something for everyone to enjoy. These lands are particularly popular for activities that allow people to connect with nature and experience the beauty of the American West.
Some of the most popular recreational activities on BLM land include:
- Hiking and Backpacking: BLM land features thousands of miles of trails, ranging from easy day hikes to challenging backcountry routes.
- Camping: Dispersed camping is allowed on most BLM land, providing a chance to experience remote wilderness areas.
- Off-Roading: Designated areas for off-highway vehicles (OHVs) cater to enthusiasts of ATVs, dirt bikes, and 4x4 vehicles.
- Wildlife Watching: BLM land is home to diverse wildlife, making it an ideal destination for birdwatching and photography.
Whether you're seeking adventure or simply a peaceful escape, BLM land offers endless possibilities for exploration and enjoyment.
Challenges and Controversies Facing BLM Land
Despite its many benefits, BLM land faces numerous challenges and controversies. These issues often stem from competing interests and the complex nature of managing such vast and diverse landscapes.
One of the most significant challenges is balancing resource extraction with conservation. While activities like mining and energy development generate economic benefits, they can also cause environmental damage and habitat loss. This has led to conflicts between industries, environmental groups, and local communities.
Another challenge is addressing the impacts of climate change. Rising temperatures, droughts, and wildfires are threatening the health and resilience of ecosystems on BLM land. The agency must adapt its management practices to mitigate these effects and protect vulnerable species and habitats.
Finally, funding limitations and staffing shortages can hinder the BLM's ability to effectively manage and protect public lands. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration, innovation, and sustained investment in land management efforts.
Conservation Efforts and Initiatives
To address the challenges facing BLM land, the agency has implemented a range of conservation efforts and initiatives. These programs aim to protect natural and cultural resources, restore degraded ecosystems, and promote sustainable land use.
One notable initiative is the BLM's focus on habitat restoration. Through partnerships with conservation organizations and local communities, the agency is working to restore critical habitats for species like the sage grouse and desert tortoise. These efforts include removing invasive species, replanting native vegetation, and improving water quality.
The BLM is also investing in renewable energy development as a way to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and support a cleaner energy future. By identifying suitable areas for solar and wind projects, the agency is helping to meet the nation’s energy needs while minimizing environmental impacts.
Additionally, the BLM is actively engaging with tribes and other stakeholders to protect cultural resources and honor the historical significance of these lands. This collaborative approach ensures that conservation efforts are inclusive and respectful of diverse perspectives.
How to Support and Protect BLM Land
Supporting and protecting BLM land is a shared responsibility that requires action from individuals, communities, and policymakers. There are many ways you can contribute to the preservation of these valuable public lands.
One of the simplest ways to support BLM land is by practicing Leave No Trace principles when visiting. This includes packing out trash, staying on designated trails, and respecting wildlife. By minimizing your impact, you help ensure that these lands remain pristine for future visitors.
You can also advocate for policies that prioritize conservation and sustainable land management. Contacting your elected representatives, participating in public comment periods, and supporting conservation organizations are effective ways to make your voice heard.
Finally, consider volunteering with local groups that work to protect and restore BLM land. Whether it’s planting trees, cleaning up trails, or monitoring wildlife, your efforts can make a meaningful difference.
Frequently Asked Questions About BLM Land
Here are some common questions and answers about BLM land:
- What is the difference between BLM land and national parks? BLM land is managed for multiple uses, including recreation, grazing, and resource extraction, while national parks are primarily focused on conservation and recreation.
- Can I camp on BLM land? Yes, dispersed camping is allowed on most BLM land, but it’s important to
JYM Vegan Protein: The Ultimate Guide To Plant-Based Muscle Building
New Bond Actor: The Next Icon Of Espionage
Ana De Armas Young: A Comprehensive Look At Her Early Career And Rise To Fame

BLM LandA Guide to Navigating and Recreating on BLM Land
BLM LandA Guide to Navigating and Recreating on BLM Land