Understanding The United States Postal System: A Comprehensive Guide
The United States Postal System (USPS) is a cornerstone of communication and commerce in America. For centuries, it has played an indispensable role in connecting people, businesses, and communities across the nation. From sending letters to delivering packages, the USPS has remained a trusted institution, even in the face of technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. In this article, we will delve into the history, operations, and significance of the USPS, offering insights into its challenges, innovations, and future prospects.
As a government agency, the USPS operates under unique constraints and responsibilities. Unlike private courier services, it is mandated to provide universal mail service to all Americans, regardless of geography or population density. This commitment to accessibility has earned the USPS its reputation as a lifeline for rural and underserved communities. However, the system has also faced criticism and financial challenges in recent years, prompting debates about its sustainability and role in the modern world.
Whether you're a business owner relying on the USPS for shipping, a consumer curious about how the postal system works, or someone interested in the history of this iconic institution, this guide will provide you with valuable insights. We will explore the USPS's origins, its operational framework, and the ways it impacts daily life. By the end of this article, you'll have a deeper understanding of why the United States Postal System remains a vital part of the nation's infrastructure.
Read also:Tire House Building Ecofriendly Homes With Recycled Materials
- The History of the United States Postal System
- How the USPS Operates Today
- Key Services Offered by the USPS
- Challenges Facing the USPS
- Innovations and Modernization Efforts
- Financial Structure and Funding
- Impact on Communities and Businesses
- The Future of the USPS
- Comparison with Private Courier Services
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the USPS
The History of the United States Postal System
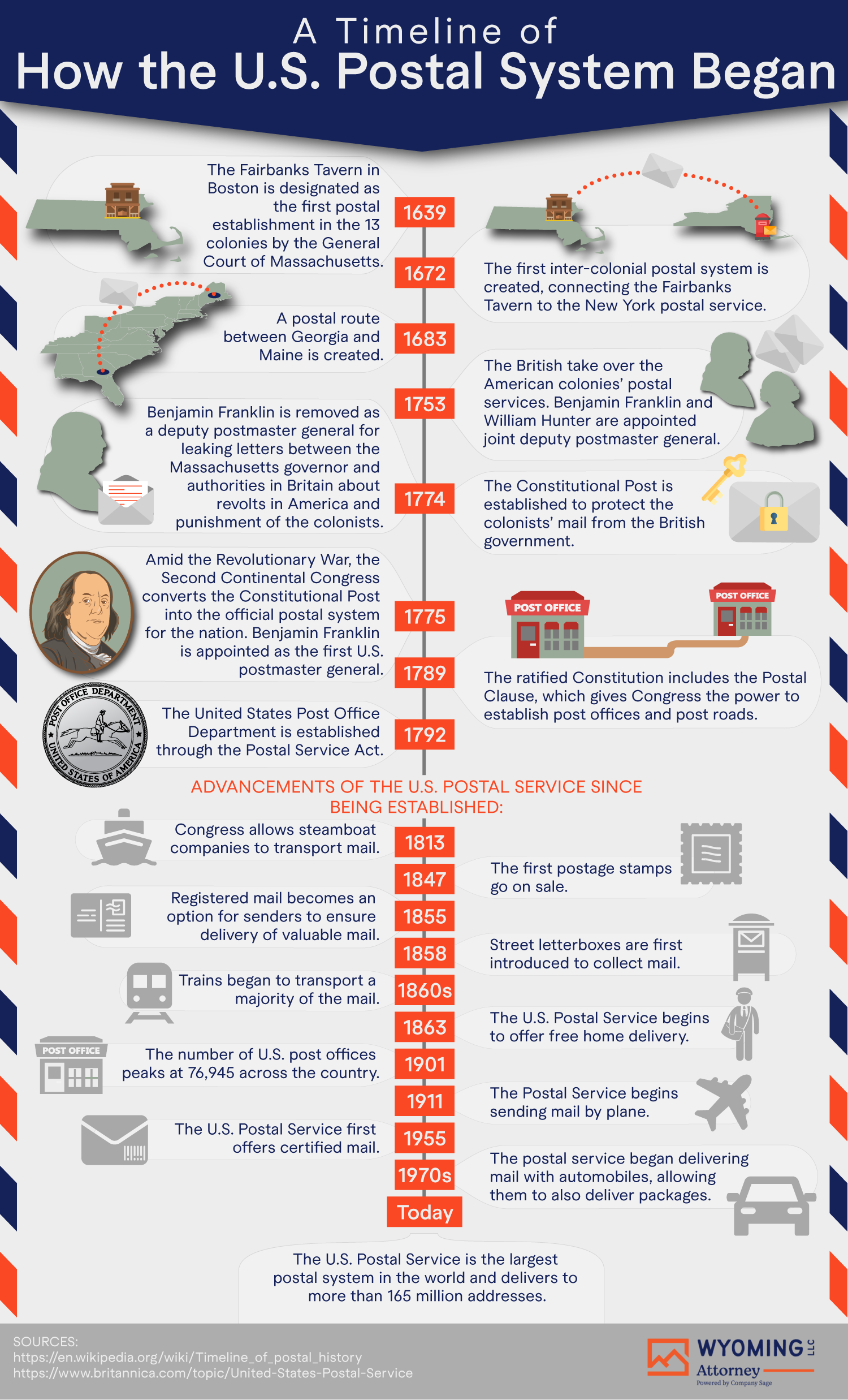
The origins of the United States Postal System can be traced back to colonial America. In 1775, Benjamin Franklin was appointed as the first Postmaster General, laying the foundation for a unified postal network. Under Franklin's leadership, the postal system expanded rapidly, connecting the thirteen colonies and facilitating communication during the Revolutionary War.
With the ratification of the U.S. Constitution in 1789, the postal system was officially established as a federal agency. The Postal Service Act of 1792 further solidified its role by granting Congress the authority to regulate and oversee postal operations. During the 19th century, the USPS played a crucial role in westward expansion, delivering mail to frontier towns and enabling the flow of information across vast distances.
The introduction of rural free delivery in 1896 marked a significant milestone, ensuring that even remote areas had access to postal services. Over the decades, the USPS has continued to evolve, adapting to technological advancements and societal changes while maintaining its commitment to universal service.
How the USPS Operates Today
Today, the USPS operates as an independent agency of the U.S. government, governed by a Board of Governors and overseen by the Postal Regulatory Commission. It employs over 600,000 workers and operates more than 31,000 post offices nationwide. Despite its size, the USPS is not taxpayer-funded; instead, it relies on revenue generated from postage and other services.
The USPS Network
The USPS operates one of the largest logistics networks in the world, processing and delivering billions of pieces of mail annually. Its operations are divided into three main categories: mail processing, transportation, and delivery. Sorting facilities, known as processing and distribution centers, handle incoming and outgoing mail, while a fleet of trucks and planes ensures timely transportation.
Delivery Services
Delivery services are a core component of the USPS's operations. From residential mailboxes to business addresses, the USPS delivers to over 160 million locations across the United States. It also offers specialized services such as Priority Mail, Express Mail, and international shipping, catering to diverse customer needs.
Read also:What Age Is Riley Green Discover The Rising Country Music Stars Age And Journey
Key Services Offered by the USPS
The USPS provides a wide range of services designed to meet the needs of individuals, businesses, and government entities. These services can be broadly categorized into mail, package, and specialized offerings.
Mail Services
Mail services include First-Class Mail, which is used for letters, postcards, and small packages. Standard Mail, on the other hand, is commonly used for advertising and bulk mailings. Both options are cost-effective and widely utilized by businesses and consumers alike.
Package Services
With the rise of e-commerce, package delivery has become a significant part of the USPS's operations. Services like Priority Mail and Priority Mail Express offer fast and reliable shipping options, while the USPS's partnership with platforms like eBay and Amazon has further bolstered its role in the logistics industry.
Challenges Facing the USPS
Despite its long history and widespread use, the USPS faces several challenges in the modern era. Financial difficulties, operational inefficiencies, and competition from private carriers have all contributed to its struggles.
Financial Challenges
One of the most pressing issues is the USPS's financial instability. In 2006, Congress passed the Postal Accountability and Enhancement Act, which required the USPS to pre-fund retiree health benefits for 75 years. This mandate placed a significant financial burden on the agency, leading to billions of dollars in losses.
Competition from Private Couriers
Private courier services like FedEx and UPS have emerged as formidable competitors, offering faster delivery times and advanced tracking capabilities. While the USPS remains the preferred choice for certain services, such as last-mile delivery, it must continually innovate to stay competitive.
Innovations and Modernization Efforts
To address these challenges, the USPS has embarked on several modernization initiatives. These efforts aim to improve efficiency, enhance customer experience, and secure the agency's future.
Technological Advancements
The USPS has invested in cutting-edge technologies, such as automated sorting systems and GPS tracking. These innovations have streamlined operations and reduced delivery times, making the postal system more efficient.
Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability is another key focus area for the USPS. The agency has introduced electric vehicles and explored alternative fuels to reduce its carbon footprint. Additionally, it has implemented recycling programs and encouraged customers to adopt paperless options where possible.
Financial Structure and Funding
Understanding the USPS's financial structure is essential to grasping its challenges and opportunities. As a self-funded agency, the USPS relies on revenue from postage and services to cover its operating costs.
Revenue Streams
The primary source of revenue for the USPS is postage sales, which account for the majority of its income. Other revenue streams include shipping services, money orders, and licensing agreements. Despite these diverse income sources, the USPS has struggled to achieve profitability due to its unique operational requirements.
Funding Challenges
Unlike other government agencies, the USPS does not receive direct taxpayer funding. This independence has both advantages and disadvantages. While it allows the agency to operate without congressional appropriations, it also limits its ability to address financial shortfalls through traditional means.
Impact on Communities and Businesses
The USPS plays a vital role in connecting communities and supporting businesses across the United States. Its universal service obligation ensures that even the most remote areas have access to mail and package delivery.
Impact on Communities
For many rural and underserved communities, the USPS is a lifeline. It delivers essential items such as medications, bills, and correspondence, enabling residents to stay connected to the broader world. The agency's presence also supports local economies by providing jobs and fostering commerce.
Impact on Businesses
Businesses of all sizes rely on the USPS for affordable and reliable shipping solutions. Small businesses, in particular, benefit from the agency's competitive pricing and extensive network. The USPS's partnerships with e-commerce platforms have further strengthened its role in the digital economy.
The Future of the USPS
As the USPS looks to the future, it faces both opportunities and challenges. Legislative reforms, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences will all shape its trajectory.
Potential Reforms
Several proposals have been put forward to address the USPS's financial challenges. These include restructuring its retiree health benefits, expanding its service offerings, and exploring public-private partnerships. While the path forward remains uncertain, these reforms could help secure the agency's long-term viability.
Growth Opportunities
The rise of e-commerce presents a significant growth opportunity for the USPS. By leveraging its extensive network and competitive pricing, the agency can continue to capture market share in the logistics industry. Additionally, its focus on sustainability and innovation positions it well for future success.
Comparison with Private Courier Services
While the USPS shares some similarities with private courier services, it also has distinct advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is key to evaluating the agency's role in the broader logistics landscape.
Advantages of the USPS
The USPS's universal service obligation sets it apart from private carriers. It is legally required to deliver to all addresses in the United States, regardless of location or profitability. This commitment ensures that even the most remote areas have access to postal services.
Disadvantages of the USPS
On the other hand, private carriers like FedEx and UPS often offer faster delivery times and more advanced tracking capabilities. They also have greater flexibility in setting prices and adjusting services to meet customer demands.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the USPS
The United States Postal System has been a cornerstone of American life for over two centuries. From its humble beginnings as a colonial mail service to its current status as a global logistics leader, the USPS has continually adapted to meet the needs of a changing world.
Despite its challenges, the USPS remains a vital institution, connecting people, businesses, and communities across the nation. Its commitment to universal service, affordability, and accessibility underscores its importance in both urban and rural areas.
As we look to the future, it is clear that the USPS will continue to play a critical role in the nation's infrastructure. Whether through legislative reforms, technological innovations, or partnerships with private entities, the agency has the potential to thrive in the years to come.
We encourage you to share your thoughts on the USPS in the comments below. Have you had a positive experience with the postal system? What changes would you like to see in the future? Don't forget to share this article with others who might find it informative and explore more content on our website!
Road Opener Prayer: Unlocking New Opportunities And Spiritual Pathways
Is Sun Good For Hair: Understanding The Benefits And Risks
El Primo Meaning In Brawl Stars: A Comprehensive Guide

USPS Logo, symbol, meaning, history, PNG, brand
The Second Continental Congress and the U.S. Postal System A Boon for