Understanding The Curve Of Wilson In Dental Anatomy: A Comprehensive Guide
The curve of Wilson is an essential concept in dental anatomy, playing a crucial role in the alignment and function of teeth. Understanding this curve is vital for dental professionals and students alike, as it influences occlusion, bite stability, and overall oral health. Whether you're studying dentistry or simply curious about dental anatomy, this guide will provide a detailed explanation of the curve of Wilson, its significance, and its applications in clinical practice.
Dental anatomy is a fascinating field that delves into the intricacies of tooth structure, alignment, and function. Among the many concepts in this discipline, the curve of Wilson stands out as a cornerstone of occlusion. This curve refers to the mediolateral curvature of the occlusal surfaces of teeth, which ensures proper alignment and contact between the upper and lower dental arches. Its role in maintaining a harmonious bite cannot be overstated.
In this article, we will explore the curve of Wilson in detail, breaking down its definition, anatomical significance, and clinical applications. We will also discuss its relationship with other dental curves, such as the curve of Spee, and provide practical insights for dental professionals. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this critical dental concept and its implications for oral health.
Read also:Jack Doherty Wife A Comprehensive Look Into His Personal Life And Marriage
Table of Contents
- What is the Curve of Wilson?
- Anatomical Significance of the Curve of Wilson
- Relationship with the Curve of Spee
- Clinical Applications in Dentistry
- Diagnosis and Treatment Considerations
- Role in Orthodontics and Prosthodontics
- Common Disorders Related to the Curve of Wilson
- Maintaining Oral Health with Proper Alignment
- Future Research and Developments
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What is the Curve of Wilson?
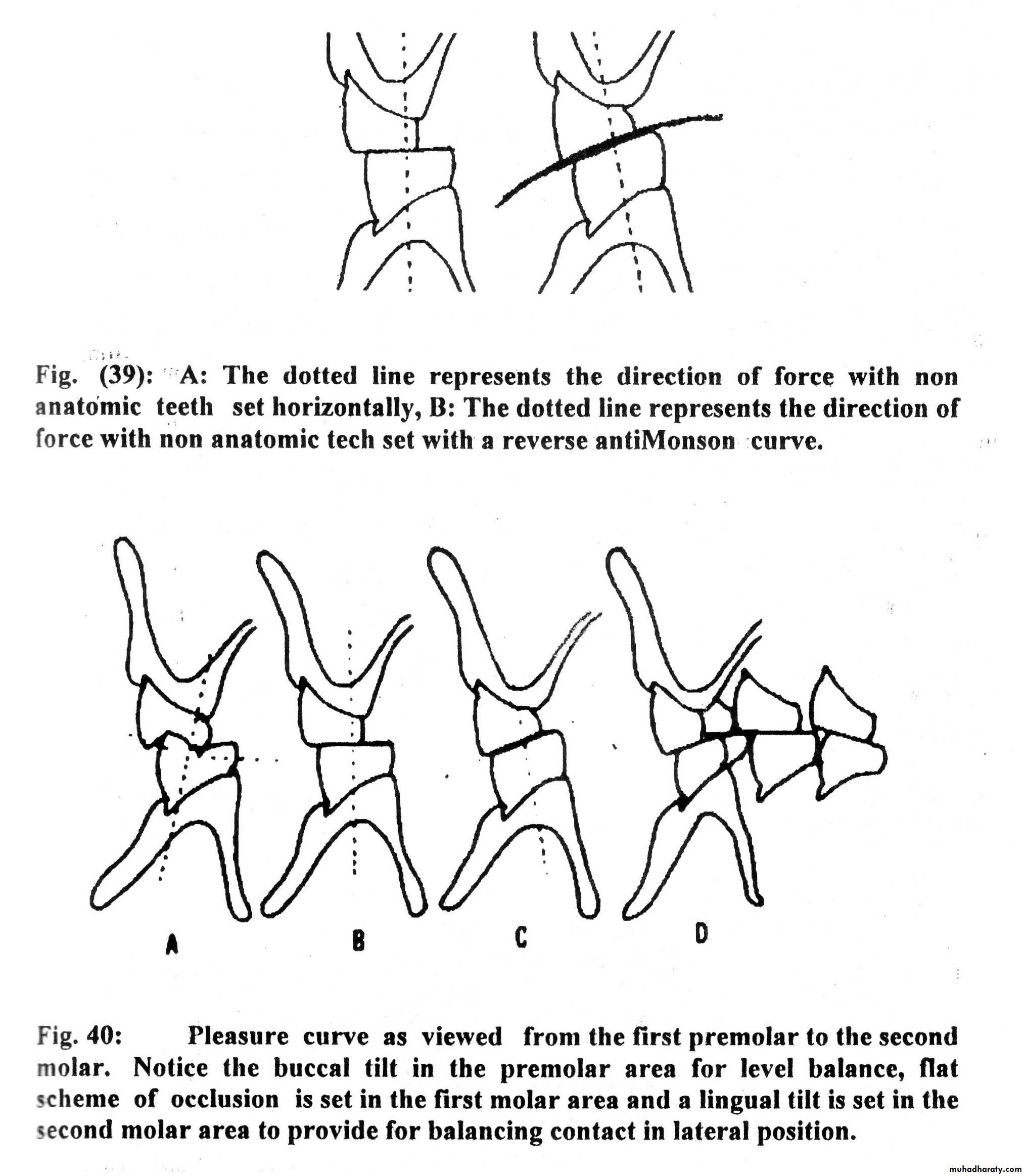
The curve of Wilson is a mediolateral curvature of the occlusal surfaces of the teeth, viewed from a frontal perspective. It is named after Dr. Alexander Wilson, who first described this anatomical feature in the context of dental occlusion. This curve is formed by the alignment of the buccal and lingual cusps of the posterior teeth, creating a smooth, curved surface that facilitates proper contact between the upper and lower dental arches.
One of the key characteristics of the curve of Wilson is its mediolateral orientation. Unlike the curve of Spee, which runs anteroposteriorly, the curve of Wilson spans across the width of the dental arch. This curvature is particularly prominent in the posterior teeth, where the buccal cusps of the maxillary teeth are positioned higher than the lingual cusps, while the opposite is true for the mandibular teeth.
Key Features of the Curve of Wilson
- Mediolateral curvature of the occlusal surfaces.
- Higher buccal cusps in the maxillary teeth.
- Higher lingual cusps in the mandibular teeth.
- Facilitates proper occlusion and bite stability.
Anatomical Significance of the Curve of Wilson
The curve of Wilson plays a vital role in the overall function of the dental arches. Its primary purpose is to ensure that the occlusal surfaces of the teeth are aligned in a way that promotes efficient chewing and minimizes stress on the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This alignment also helps distribute occlusal forces evenly across the teeth, reducing the risk of wear and damage.
In addition to its functional role, the curve of Wilson contributes to the aesthetic appearance of the smile. Proper alignment of the teeth along this curve enhances the symmetry and harmony of the dental arches, creating a visually pleasing smile. Dental professionals often consider this curve when planning orthodontic treatments or designing dental prostheses.
Impact on Occlusion and Bite Stability
- Ensures proper contact between upper and lower teeth.
- Reduces stress on the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
- Distributes occlusal forces evenly.
- Minimizes the risk of tooth wear and fractures.
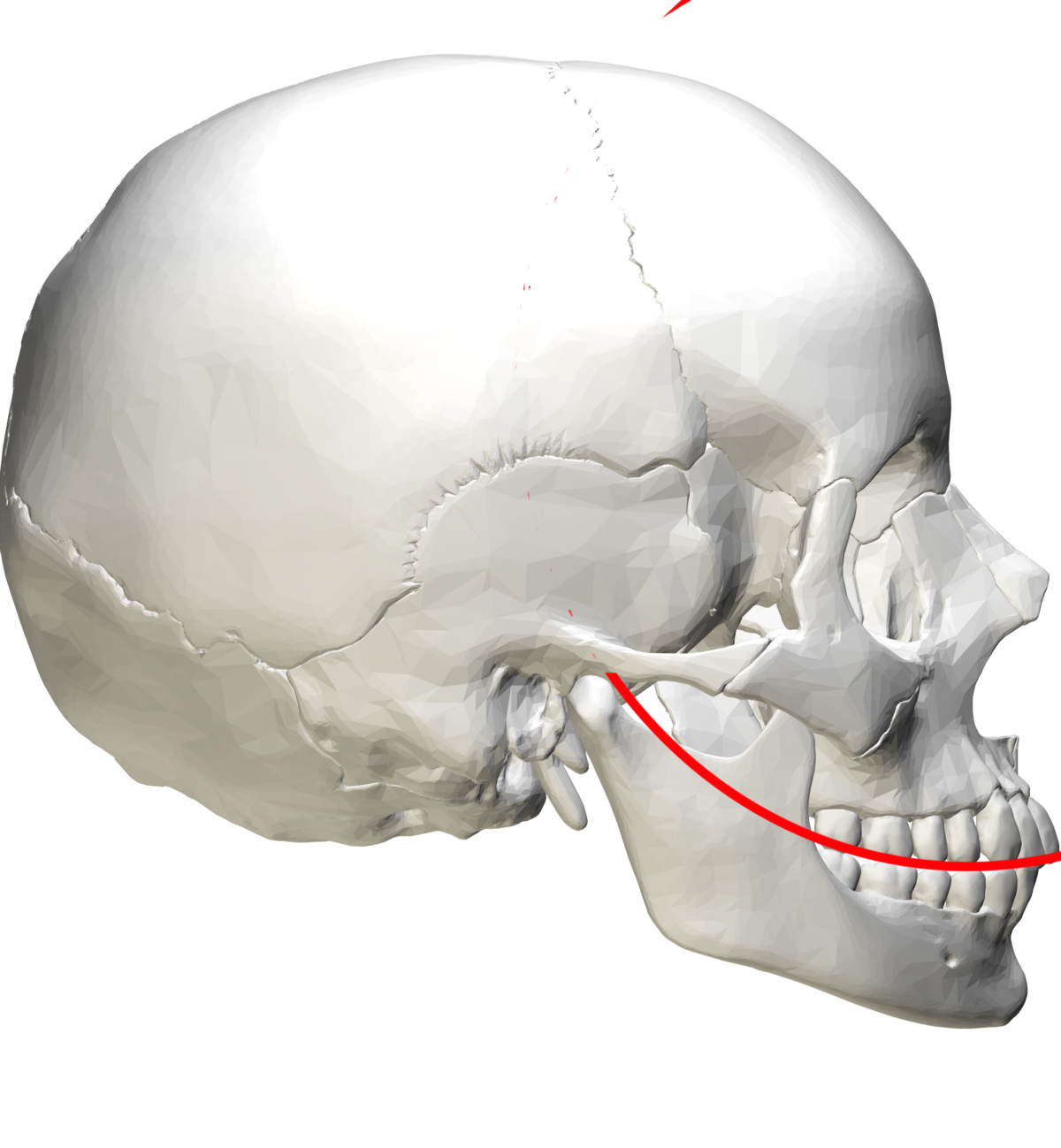
Relationship with the Curve of Spee
The curve of Wilson is closely related to another important dental curve: the curve of Spee. While the curve of Wilson is mediolateral, the curve of Spee runs anteroposteriorly, forming a sagittal curvature of the occlusal surfaces. Together, these two curves create a three-dimensional alignment of the teeth that is essential for proper occlusion.
Understanding the relationship between these curves is crucial for diagnosing and treating malocclusions. For example, an excessive curve of Spee may indicate a deep bite, while an exaggerated curve of Wilson could suggest a crossbite. By analyzing both curves, dental professionals can develop comprehensive treatment plans that address all aspects of occlusal alignment.
Read also:Hosts Of Outnumbered A Comprehensive Guide To The Shows Dynamic Personalities
Comparing the Two Curves
- Curve of Wilson: Mediolateral curvature.
- Curve of Spee: Anteroposterior curvature.
- Both curves contribute to three-dimensional alignment.
- Analysis of both curves aids in diagnosing malocclusions.
Clinical Applications in Dentistry
The curve of Wilson has numerous clinical applications in various fields of dentistry, including orthodontics, prosthodontics, and restorative dentistry. In orthodontics, understanding this curve is essential for diagnosing and correcting malocclusions. Orthodontists often use this knowledge to design treatment plans that achieve proper alignment of the teeth and improve bite stability.
In prosthodontics, the curve of Wilson is considered when designing dental prostheses such as crowns, bridges, and dentures. Ensuring that these prostheses align with the natural curvature of the teeth is crucial for achieving optimal function and aesthetics. Similarly, in restorative dentistry, the curve of Wilson guides the placement of restorative materials to maintain proper occlusion.
Applications in Different Dental Fields
- Orthodontics: Correcting malocclusions.
- Prosthodontics: Designing dental prostheses.
- Restorative Dentistry: Placing restorative materials.
- General Dentistry: Maintaining occlusal harmony.
Diagnosis and Treatment Considerations
Diagnosing issues related to the curve of Wilson requires a thorough clinical examination and the use of diagnostic tools such as dental casts, radiographs, and digital imaging. Dental professionals assess the alignment of the teeth, the curvature of the occlusal surfaces, and the relationship between the upper and lower dental arches.
Treatment options vary depending on the specific issue. For example, orthodontic appliances such as braces or clear aligners may be used to correct an exaggerated curve of Wilson. In cases where the curve is affected by missing teeth, dental implants or prostheses may be recommended to restore proper alignment. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to achieving optimal outcomes.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
- Dental casts for physical assessment.
- Radiographs and digital imaging.
- Clinical examination of occlusal surfaces.
- Analysis of dental arch alignment.
Role in Orthodontics and Prosthodontics
The curve of Wilson is particularly significant in orthodontics and prosthodontics, where achieving proper occlusion is a primary goal. In orthodontics, this curve is used as a reference point for aligning the teeth and correcting malocclusions. Orthodontists aim to achieve a balanced curve of Wilson to ensure that the teeth function harmoniously and that the bite is stable.
In prosthodontics, the curve of Wilson guides the design and placement of dental prostheses. Whether it's a single crown or a full denture, the prosthesis must align with the natural curvature of the teeth to ensure proper function and aesthetics. Failure to consider this curve can result in occlusal interference, discomfort, and reduced longevity of the prosthesis.
Importance in Prosthesis Design
- Alignment with natural curvature.
- Ensuring proper occlusion and function.
- Enhancing aesthetic outcomes.
- Preventing occlusal interference.
Common Disorders Related to the Curve of Wilson
Several dental disorders are associated with abnormalities in the curve of Wilson. One common issue is a crossbite, where the buccal cusps of the maxillary teeth do not align properly with the lingual cusps of the mandibular teeth. This condition can lead to uneven wear, discomfort, and TMJ disorders if left untreated.
Another disorder is an exaggerated curve of Wilson, which may result from malpositioned teeth or skeletal discrepancies. This condition can affect bite stability and increase the risk of occlusal trauma. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent long-term complications and restore proper alignment.
Examples of Disorders
- Crossbite: Misalignment of buccal and lingual cusps.
- Exaggerated curve: Skeletal discrepancies.
- Occlusal trauma: Increased risk of tooth damage.
- TMJ disorders: Stress on the temporomandibular joint.
Maintaining Oral Health with Proper Alignment
Maintaining proper alignment of the teeth along the curve of Wilson is essential for long-term oral health. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can help identify and address issues early, preventing complications such as malocclusions and TMJ disorders. Dental professionals may recommend orthodontic treatment or other interventions to correct alignment issues and restore occlusal harmony.
In addition to professional care, individuals can take steps to maintain their oral health at home. This includes practicing good oral hygiene, avoiding habits that can affect tooth alignment (such as thumb-sucking), and wearing protective appliances if recommended by a dentist. By prioritizing oral health, individuals can enjoy a functional and aesthetically pleasing smile for years to come.
Tips for Maintaining Alignment
- Regular dental check-ups and cleanings.
- Orthodontic treatment for alignment issues.
- Good oral hygiene practices.
- Avoiding harmful habits.
Future Research and Developments
As dental science continues to advance, researchers are exploring new ways to understand and address issues related to the curve of Wilson. Innovations in digital dentistry, such as 3D imaging and computer-aided design, are providing dental professionals with more precise tools for diagnosing and treating malocclusions. These technologies are also enhancing the accuracy of prosthesis design and placement.
Future research may focus on the genetic and environmental factors that influence the development of the curve of Wilson. By gaining a deeper understanding of these factors, dental professionals can develop more personalized treatment plans and improve outcomes for patients. Additionally, advancements in materials science may lead to the development of more durable and aesthetically pleasing dental prostheses.
Emerging Trends in Dental Science
- 3D imaging and computer-aided design.
- Personalized treatment plans.
- Advancements in materials science.
- Research on genetic and environmental factors.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the curve of Wilson is a fundamental concept in dental anatomy that plays a critical role in occlusion, bite stability, and overall oral health. Understanding this curve is essential for dental professionals and students, as it influences various aspects of clinical practice, from orthodontics to prosthodontics. By maintaining proper alignment along the curve of Wilson, individuals can enjoy a functional and aesthetically pleasing smile.
If you found this article informative, we encourage you to share it with others who may benefit from this knowledge. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts or ask questions, and explore our other articles for more insights into dental health and anatomy. Together, let's promote better oral health and understanding for everyone.
The Importance Of Tennis Grand Slam Tournaments In The Sports World
Fleabag Haircut: The Trendy, Edgy Look Taking Over Hairstyles In 2023
Novant Health Presbyterian: A Leading Healthcare Provider In The Southeast
occlusion pptx Dr.Munia Muhadharaty
Curva De Spee Acentuada